Remyelination models
Myelin repair (i.e. remyelination) restores the functional integrity of axons and is neuroprotective. Our remyelination models capture several important attributes of Multiple sclerosis and has been successfully used to test remyelination therapeutics.
The most commonly used models used to study remyelination biology and pathology is the focal Lysophosphatidylcholine-induced Remyelination model and the Cuprizone Remyelination model.
Cuprizone Model of Remyelination
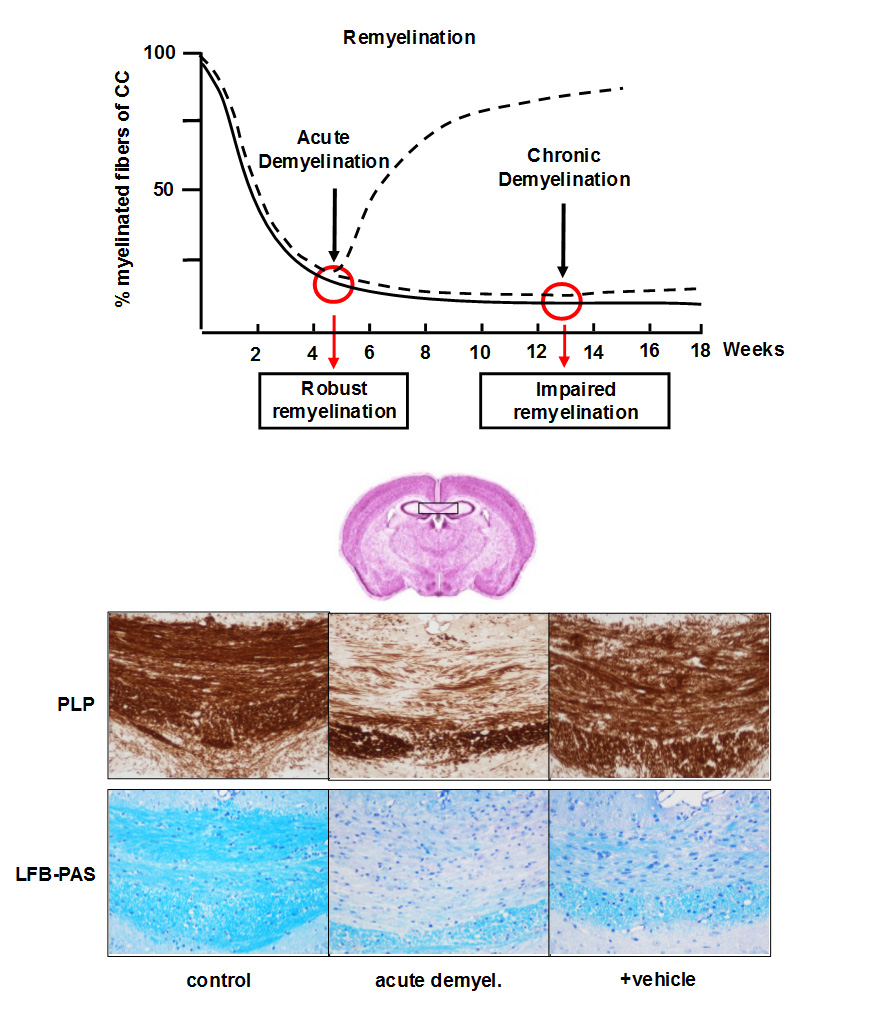
Cuprizone ingestion in mice induces a highly reproducible demyelination of distinct brain regions, among them the corpus callosum which represents the most frequently investigated white matter tract in this animal model. After 5–6 weeks of cuprizone treatment, the Corpus callosum is almost completely demyelinated, a process called ‘‘acute demyelination’’. Acute demyelination is followed by spontaneous remyelination during subsequent weeks when mice are fed normal chow.
In contrast, remyelination is highly restricted when cuprizone administration is prolonged (13 weeks or longer), a process called ‘‘chronic demyelination’’. To study the effectiveness of pharmaceutical substances on myelin repair, acute or chronic demyelination will be induced in mice and animals treated during the recovery period. Test compound can be delivered either per os, intravenously, intraperitonealy, intraventricularily by stereotaxis, or by subcutaneous depot-injections.

Experimental setting for stereotactic surgery to induce focal demyelination
Focal Lysophosphatidylcholine-induced Remyelination model
Demyelination is induced by focal application of the toxin Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC). LPC disrupts membranes, including myelin, by inserting into lipid bilayers to form micelles. LPC-induced demyelination is followed by spontaneous, endogenous remyelination. For a reliable and reproducible intracerebral LPC injection, we perform stereotactic surgeries and use an automatic Ultra Micro Pump.
Each injection will be carried out within a standardized time frame, to prevent potential variations in the effect of shearing forces. To study the effectiveness of pharmaceutical substances on myelin repair, demyelination will be induced in mice and animals treated during the recovery period. Test compound can be delivered either per os, intravenously, intraperitonealy, intraventricularily by stereotaxis, or by subcutaneous depot-injections.
Experimental End Points
- Quantification of myelination in diverse brain regions
- Additional histological quantification (OPCs, oligodendrocytes, microglia, etc)
- Quantification of myelin protein expression levels
- Electron microscopy evaluation of distinct myelin and axonal parameters